LAMOST released its Seventh Data (DR7) internationally
On September 30, 2021, LAMOST published its Seventh Data Release (DR7 v2.0) to astronomers worldwide, which includes the spectra obtained from the pilot survey through the seven-year regular survey from October 2011 to June 2019.
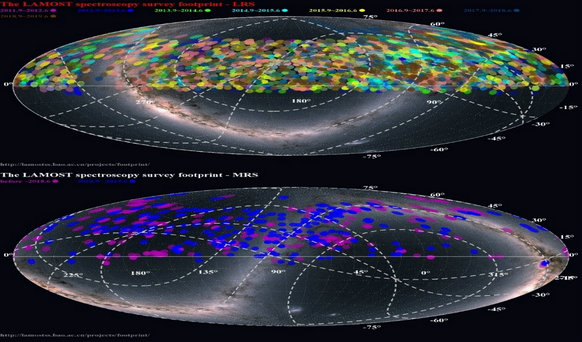
Figures: (Top) Footprint of the LAMOST pilot survey and the seven-year regular low-resolution survey; (Bottom) Footprint of the LAMOST medium-resolution commissioning and the first-year regular medium-resolution survey. (Credit: LAMOST)
The released DR7 dataset (v2.0) includes both the regular low-resolution spectral data and medium-resolution spectral data. Obtained from the low-resolution observation of 4,922 plates and medium-resolution observation of 679 plates, a total of 14.23 million spectra are released in the DR7 (v2.0), including 10.43 million low-resolution spectra, 0.98 million medium-resolution non-time-domain spectra and 2.82 million medium-resolution time-domain spectra. The number of high-quality (S/N>10) spectra reach 11.35 million. Moreover, a stellar spectral parameter catalogue of 6.91 million stars is also released this time, which has been currently the largest stellar spectral parameter catalogue in the world. Scientific users can log on the website at http://dr7.lamost.orgto query and download the DR7 (v2.0) data.
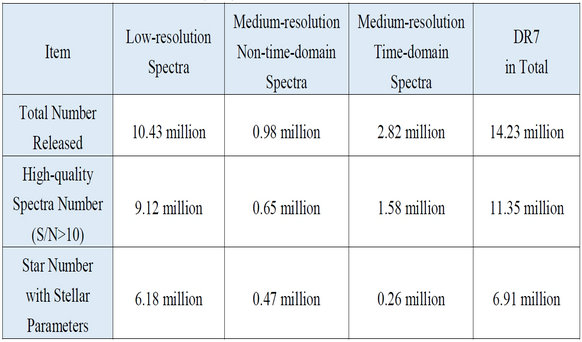
Table: Information of DR7 dataset (v2.0).
After the DR7 v1.0 was released to domestic astronomers and international partners in March 2020, the Data Processing Department of LAMOST Operation and Development Center has updated and optimized the DR7 dataset twice using the upgraded data processing software, and the corresponding datasets of DR7 v1.2 and DR7 v1.3 have been released, successively. On this basis, the DR7 v2.0 dataset released this time has been further updated as follows: (1) the catalogues of confirmed cataclysmic variable stars, white dwarf stars and sub-dwarf stars were added; (2) the temperature range of stellar parameters was expanded to 8500K-18000K. The accuracy of LAMOST data has reached the international advanced level.
The spectral data and related products of LAMOST provide valuable insights for the studyof the Galactic structure, origin and evolution, stellar physics, special and compact celestial objects, quasars, and so on. With the continuous efforts of the LAMOST team and the mining and use of LAMOST data by astronomers all over the world, LAMOST will continue to show more excitement.